Key Takeaways
-
Cryptocurrency is digital or virtual money.
-
It operates independently of traditional financial institutions.
-
Transactions are secured using advanced cryptographic methods.
-
Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency.
-
There are many types of cryptocurrencies, each with different characteristics.
Cryptocurrency is a complex but exciting topic. Think of it as digital money. It works differently from regular money. In this guide, we’ll keep it simple. You’ll learn what cryptocurrency is. We’ll explain how it works. You’ll see why it matters.
Defining Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency can be described as digital cash. Unlike traditional currencies, it isn’t managed by a government or financial institution. Instead, it exists in an online environment and uses technology to operate. This form of digital cash is called cryptocurrency because it relies on cryptographic methods to secure transactions.
Also known as virtual currencies, cryptocurrencies can be used to purchase goods and services or as an investment. Transactions occur online, making them fast and borderless.
As of August 2024, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization is approximately $1.2 trillion, a significant decrease of 14.4% from the beginning of the year due to market fluctuations.
Understanding Cryptocurrency Fundamentals
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital asset. It operates on a decentralized network, meaning no single entity controls it. Instead, these digital currencies rely on a distributed network of computers. This network uses peer-to-peer technology to facilitate transactions.
The first cryptocurrency was Bitcoin, created in 2009 by an anonymous individual or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin was designed as a peer-to-peer electronic payment system that doesn’t require banks. This groundbreaking concept sparked the development of numerous other cryptocurrencies, commonly referred to as altcoins.
Cryptocurrencies are stored in digital wallets, specialized software designed to secure your digital funds. When you want to spend or transfer cryptocurrency, your wallet digitally signs the transaction.
The Mechanics of Crypto
Cryptocurrencies are powered by blockchain technology. Think of a blockchain as a shared, digital ledger that records every transaction. This ledger is spread across many computers, called nodes, ensuring security and transparency.
Building the Blockchain
- Each new transaction is added as a “block.”
- When a block fills, it links to the last one, creating a chain of blocks — the blockchain.
- This chain keeps growing, recording each new transaction in a secure, unbreakable sequence.
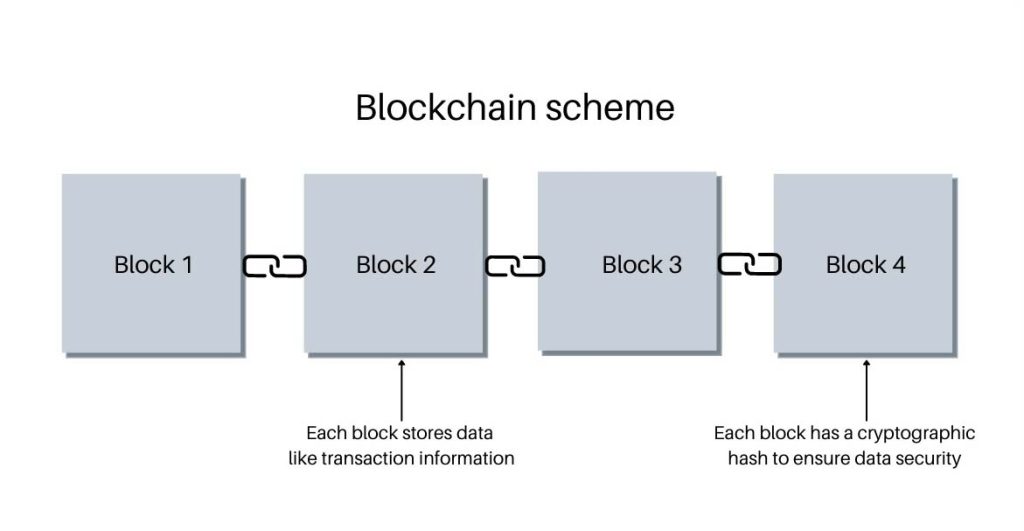
Building the Blockchain
The Role of Cryptography
Cryptography acts as a hidden code, securing every transaction. Only the rightful owner can access their cryptocurrency, thanks to this protection. Cryptography is vital to keeping transactions safe.
Mining: Adding New Blocks
Mining is another key part of cryptocurrency. Miners are computers that solve complex math problems:
- When they solve a problem, a new block joins the chain.
- Miners are rewarded with new cryptocurrency for each successful block.
Verifying Transactions: Consensus Mechanism
To add a transaction to the blockchain, the network must agree on its validity. This process, called consensus, ensures every transaction is secure and authentic, maintaining the system’s reliability.
In 2024, centralized exchanges recorded $3.4 trillion in spot trading volume in Q2, marking a 12.2% decrease from the previous quarter.
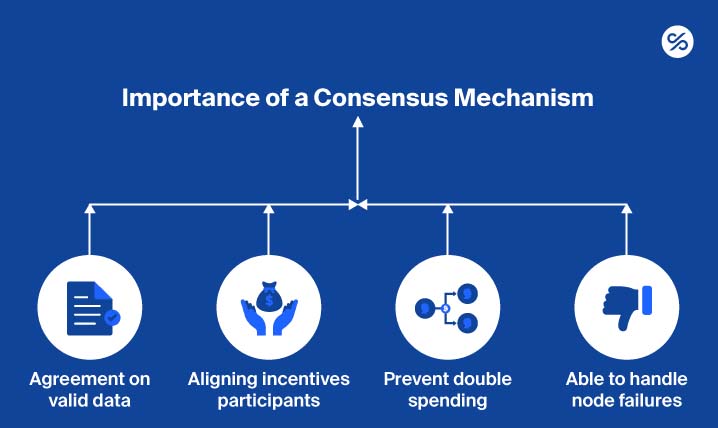
Verifying Transactions: Consensus Mechanism
Blockchain Technology: The Foundation of Cryptocurrency
The blockchain is not centralized, but distributed across many computers around the world. These computers, or nodes, work together to maintain the blockchain. Its decentralized nature enhances the security of the blockchain, ensuring that no single entity can alter the information within the blocks without being detected.
Data integrity is a critical aspect of blockchain technology. This means that once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be changed. This feature makes the blockchain highly reliable.
As of August 2024, Solana’s blockchain has experienced a significant increase in activity, with its price rising by 30.5%, driven by an 18.2% surge in daily transactions.
Here’s the graph showing the increase in activity and price of the Solana blockchain from June to August 2024:
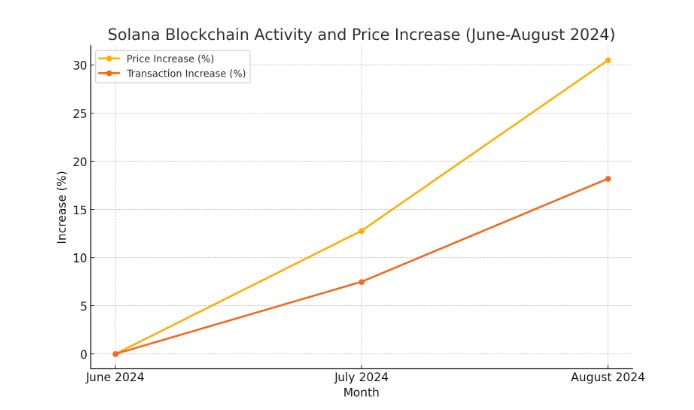
Blockchain Technology: The Foundation of Cryptocurrency
Varieties of Cryptocurrency
Bitcoin: The Pioneer
Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency to emerge and remains the most recognized. It was developed in 2009 by an enigmatic individual or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin introduced the groundbreaking concept of a decentralized digital currency. It operates on a blockchain that records all transactions involving Bitcoin.
Bitcoin, often referred to by its ticker symbol BTC, has a finite supply — only 21 million Bitcoins will ever exist. This scarcity contributes to its value. Many individuals invest in Bitcoin, expecting its value to increase over time.
The creation of Bitcoin paved the way for the development of other cryptocurrencies.
Beyond Bitcoin — Altcoins
Altcoins are any cryptocurrencies other than Bitcoin. The term “altcoin” is short for “alternative coin.” Thousands of altcoins exist, each offering distinct features.
| Cryptocurrency | Description |
| Ethereum (ETH) | More than a cryptocurrency; a platform for decentralized applications (DApps). Facilitates smart contracts, enabling self-executing agreements. |
| Ripple (XRP) | Focuses on cross-border payments with its digital payment protocol. Favored by financial institutions. |
| Litecoin (LTC) | Often called the “silver” to Bitcoin’s “gold.” Created for faster, cheaper transactions with a unique mining algorithm. |
| Cardano (ADA) | Aims to provide secure, scalable digital value transfer. Developed by Charles Hoskinson, Ethereum’s co-founder. |
| Polkadot (DOT) | Connects multiple blockchains, enabling interoperability. Enhances collaboration between different blockchains. |
Altcoins offer various functionalities, making them appealing for different use cases. Some are faster than Bitcoin, while others provide additional features like smart contracts.
Stablecoins: Stability in a Volatile Market
Stablecoins are a unique category of cryptocurrency designed to maintain a stable value. They are often pegged to a stable asset, such as the US dollar. This stability makes them practical for everyday transactions, unlike other cryptocurrencies that can exhibit extreme price volatility.
- Tether (USDT): Tether is one of the most widely used stablecoins. It is pegged to the US dollar, meaning 1 USDT typically equals 1 USD.
- USD Coin (USDC): Another popular stablecoin, USDC, is also pegged to the US dollar and is extensively used within the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Stablecoins offer the benefits of cryptocurrency — fast transactions and minimal fees — without the risks associated with price volatility. In 2024, stablecoins will remain an important part of the crypto ecosystem, with continued demand even amidst market instability.
Utility Tokens: Accessing Digital Services
Utility tokens give access to specific platform services. They aren’t mainly for investing but provide service access.
Examples of Utility Tokens:
- Binance Coin (BNB): BNB is for Binance exchange fees. Users get discounts when paying fees with BNB.
- Filecoin (FIL): FIL is used on Filecoin’s storage network. Users pay FIL to store and retrieve data.
- Basic Attention Token (BAT): BAT is for rewards in the Brave browser. Advertisers pay users with BAT for ad views.
- Chainlink (LINK): LINK is for Chainlink’s data service. LINK pays “oracles” for providing real-world data.
These tokens are mainly for platform interaction, helping users access unique platform features instead of acting as investments.
Security Tokens: Digital Assets with Real-World Value
Security tokens are investments tied to real assets, like company shares or real estate. They are under regulatory oversight because they represent securities.
Examples of Security Tokens:
- tZERO (TZROP): tZERO is a platform for trading digital securities. TZROP token holders get a share of company profits.
- Harbor (R-Token): Harbor’s R-Token is used for tokenized real estate. Investors can own a part of real estate assets.
- Securitize (DS Tokens): Securitize issues DS tokens for companies. These tokens represent ownership in various companies.
- Aspen Coin: Aspen Coin represents ownership in the St. Regis Aspen Resort. Investors can own a part of this luxury resort.
Unlike utility tokens, security tokens represent ownership. They provide holders with real-world value, rights, and ownership benefits.
Choosing a Cryptocurrency Exchange
Сryptocurrency exchanges are digital marketplaces where you can buy and sell cryptocurrencies. With numerous options available, each exchange has its own strengths and weaknesses.
- Binance: One of the largest and most diverse exchanges, offering a broad range of cryptocurrencies with competitive fees. As of 2024, Binance remains the leading centralized exchange, commanding 45% of the market share.
- Coinbase: Known for its user-friendly interface, Coinbase is particularly popular among newcomers. It offers a simple, secure platform for buying and selling cryptocurrencies.
- Kraken: A well-established exchange that prioritizes security, Kraken offers a wide selection of cryptocurrencies and advanced trading features.
When choosing an exchange, consider factors such as security, fees and the range of cryptocurrencies available. Some exchanges are designed for beginners, while others are more suitable for experienced traders.
Protecting Your Cryptocurrency: Best Digital Wallets for 2024
A digital wallet is a tool that stores your cryptocurrencies. There are different types of wallets, each offering unique security features.
- Hardware Wallets: These physical devices store your cryptocurrencies offline, making them highly secure against online threats. In 2024, devices like Ledger and Trezor remain top choices for those seeking maximum security.
- Software Wallets: These applications store your cryptocurrency online. While convenient, they are more vulnerable to hacking compared to hardware wallets. Popular options include MetaMask and Trust Wallet.
- Paper Wallets: These are printed documents that contain your public and private keys. While they are immune to online hacking, they need to be stored securely to prevent physical theft.
Choosing the right wallet depends on your security needs. Hardware wallets offer the highest level of protection at a higher cost, while software wallets offer convenience with some security compromises.
Cryptocurrency Legal and Regulatory Landscape in 2024
Cryptocurrency regulation varies significantly across different regions. In some countries, it is fully legal and regulated, while in others, it faces restrictions or outright bans.
- United States: In the US, cryptocurrency is legal but regulated. The IRS classifies it as property for tax purposes. Different states have their own regulatory frameworks, with Wyoming known for its favorable crypto laws, while New York’s BitLicense imposes stricter requirements on exchanges.
- Europe: The European Union is gradually developing a unified regulatory framework for cryptocurrency. Countries like Germany and Switzerland have clear regulations, while others are still in the process of establishing their guidelines.
- Asia: The legal status of cryptocurrency in Asia varies widely. Japan is recognized for its crypto-friendly regulations, whereas China has banned most cryptocurrency-related activities. India is still working on a clear regulatory framework for digital assets.
Regulatory Bodies and Compliance
Several regulatory bodies oversee the cryptocurrency industry to ensure its legal and safe use.
- SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission): In the United States, the SEC regulates securities, including certain types of cryptocurrency activity, particularly those involving initial coin offerings (ICOs).
- FCA (Financial Conduct Authority): The FCA regulates financial markets in the UK. It provides guidance to cryptocurrency businesses to ensure compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) laws.
- FINMA (Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority): FINMA regulates Switzerland’s financial markets, which are among the most crypto-friendly in the world. It provides clear regulatory guidance for cryptocurrency businesses.
Cryptocurrency Safety Tips and Risk Mitigation Strategies
Here are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Attackers are increasingly using sophisticated methods such as phishing and impersonation to gain unauthorized access to accounts. In 2024, security experts advocate non-phishable multifactor authentication (MFA) solutions, such as hardware tokens like Yubikeys, which offer stronger protection than traditional SMS-based 2FA.
- Use Cold Storage: In 2022, cryptocurrency companies will lose approximately $3.8 billion to hacks, with DeFi protocols being the most vulnerable. Despite a slight decrease in hacking incidents in 2023, the risk remains significant, and offline cold wallets provide an important layer of security by protecting private keys from online threats.
- Create Strong Passwords: The increased use of generative AI in 2024 has made it easier for attackers to create convincing phishing attempts, making it even more important to avoid password reuse and rely on password managers to securely manage complex passwords.
Create Strong Passwords
Understanding Cryptocurrency Risks: Common Challenges in 2024
Investing in cryptocurrency comes with its risks. Here are some of the most common ones:
- Hacks: Bad guys on the internet love to steal digital money. In 2024, they took over $14 billion by hacking into online wallets and exchanges. So, it’s important to keep your money safe!
- Scams: Sometimes people pretend to be your friend online, but they are just trying to trick you. They might tell you about a cool way to make a lot of money fast, but it’s a lie. Be wary of anything that sounds too good to be true!
- Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices go up and down very quickly, like a rollercoaster. For example, the price of Bitcoin went from $30,000 to $72,000 in just a few months. This means you could make a lot of money or lose a lot of money very quickly.
Smart Cryptocurrency Investment Strategies for 2024
While the potential rewards of cryptocurrency investment are substantial, the risks are equally significant. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Conduct Thorough Research: Always research a cryptocurrency before investing. Understand its technology, use case, and development team.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Don’t invest all your funds in one cryptocurrency. Spread your investments across various assets to reduce risk.
- Adopt a Long-Term Perspective: Cryptocurrency is still a nascent industry. Short-term price volatility is common, so it’s wise to maintain a long-term view.

Advantages of Cryptocurrency
Advantages of Cryptocurrency
-
The Appeal of Decentralization
One of the key benefits of cryptocurrency is decentralization. Unlike traditional money, which is controlled by governments and financial institutions, cryptocurrency operates on a decentralized network of computers.
This decentralization offers many benefits, including reduced risk of censorship and greater control over personal finances. Decentralization also increases the security of the system, as there is no single point of failure.
-
Lower Transaction Costs
Cryptocurrency transactions are often more cost-effective than traditional financial transactions due to the absence of intermediaries like banks.
For example, sending money across borders through traditional means can incur high fees. Cryptocurrency transactions generally have lower fees, making them a cost-efficient option for cross-border payments.
-
Financial Accessibility
Cryptocurrency has the potential to enhance financial inclusion, particularly for individuals who lack access to traditional banking services.
In many developing regions, where banking infrastructure is limited, cryptocurrency provides a secure and accessible way to store and transfer money without needing a bank account.
Disadvantages of Cryptocurrency
-
Navigating Price Fluctuations
A major disadvantage of cryptocurrencies is their price volatility. Cryptocurrency values can change rapidly, making them a high-risk investment.
For example, the price of Bitcoin has been known to fluctuate by thousands of dollars in a single day. This volatility makes it difficult to use cryptocurrencies as a stable store of value or a reliable medium of exchange.
-
Uncertain Regulatory Environment
The regulatory framework surrounding cryptocurrency is still evolving, creating uncertainty for investors and businesses. Regulations vary widely across countries, making global operations challenging.
Some countries have embraced cryptocurrencies, while others have banned them. This uncertainty can affect the adoption and value of cryptocurrencies.
-
Environmental Impact
Cryptocurrency mining, especially for Bitcoin, requires significant energy consumption, raising environmental concerns.
For example, the energy consumption of the Bitcoin network is comparable to that of some entire countries. This has led to increased scrutiny and calls for more sustainable mining practices.
Real-World Applications of Cryptocurrency in 2024

Real-World Applications of Cryptocurrency in 2024
-
Everyday Payments and Transactions
Cryptocurrency is increasingly being used for everyday payments and transactions, offering benefits such as lower fees and faster processing times compared to traditional methods.
Some merchants now accept Bitcoin as a form of payment, allowing customers to use cryptocurrency to purchase goods and services.
-
Investment and Market Trading
Cryptocurrency is also a popular investment vehicle. Many investors purchase cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, hoping for price appreciation over time.
Additionally, cryptocurrency trading has become a lucrative activity, where traders buy and sell cryptocurrencies on exchanges to profit from price fluctuations.
-
Smart Contracts: Automation in Action
Smart contracts are one of the most innovative uses of cryptocurrency. These self-executing contracts have terms written directly into the code, allowing various processes to be automated without the need for intermediaries.
Ethereum, for example, is a platform that supports smart contracts, allowing developers to create decentralized applications (DApps) that run on the blockchain.
-
The Rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized finance, or DeFi, represents a new financial ecosystem built on blockchain technology. It aims to replicate traditional financial services, such as lending and borrowing, without the need for banks.
Platforms like Compound and Aave allow users to lend and borrow cryptocurrencies directly from one another. This system increases access to financial services and eliminates the need for traditional intermediaries. In July 2024, the total value locked in DeFi protocols saw a 3.5% increase, demonstrating its resilience amid market fluctuations.
Cryptocurrency Future Trends and Predictions for 2024

Cryptocurrency Future Trends and Predictions for 2024
The future of cryptocurrency appears promising. Technological advancements are driving increased adoption. Experts predict mainstream payment integration. Some view it as a valuable investment.
Emerging trends are shaping the landscape:
- DeFi Growth: Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is expanding rapidly. In July 2024, DeFi protocols saw a 3.5% increase in total value locked, demonstrating resilience amid market fluctuations.
- Stablecoin Usage: Stablecoins are gaining traction. They offer stability in volatile markets. In 2024, stablecoins remain an important part of the crypto ecosystem, with continued demand even amidst market instability.
- Institutional Adoption: Major institutions are embracing crypto. This adds legitimacy to the market. In August 2024, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization was approximately $1.2 trillion, a significant decrease of 14.4% from the beginning of the year due to market fluctuations.
- Regulatory Developments: Governments are crafting crypto regulations. This aims to balance innovation and security. In the second quarter of 2024, centralized exchanges recorded a total spot trading volume of $3.4 trillion, down 12.2% from the previous quarter.
Challenges persist, including regulatory uncertainty and environmental concerns. Addressing these is crucial for sustainable growth.
In conclusion, cryptocurrency is poised to transform finance. Its role in payments, investments, and services is set to expand.
What is cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is like digital money. It’s protected by special codes and doesn’t need banks or governments to work.
How does cryptocurrency work?
Cryptocurrency works through a technology called blockchain. Think of it as a big book where all transactions are recorded. These records are protected by codes so no one can change them.
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is the first and most widely known cryptocurrency, created in 2009. It operates on a blockchain, and as of August 2024, its price is approximately $62,734.
What are altcoins?
Altcoins are any cryptocurrencies other than Bitcoin. They include Ethereum, Ripple, Litecoin, and many others. In 2024, some altcoins like Solana have demonstrated significant growth, with a 30.5% price increase in July.
Is cryptocurrency legal?
Cryptocurrency laws are different around the world. In some places, it’s allowed, while in others, there are strict rules or bans. In the U.S., it’s legal but regulated.
How does cryptocurrency gain value?
Cryptocurrency value mostly depends on supply and demand. When more people buy a cryptocurrency, its value can rise. Things like news, technology changes, and laws can also impact its price.
What are the risks of using cryptocurrency?
Using cryptocurrency has risks like big price changes, hacking, and uncertain laws. Prices can jump up or down fast, and keeping crypto safe can be tricky.
Is cryptocurrency a good investment in 2024?
Cryptocurrency can be both high-risk and high-reward. In 2024, there are good opportunities like DeFi and growing regulations, but price changes and new laws can affect investments.
How can I start with cryptocurrency safely?
To start safely, pick a trusted exchange, use a secure wallet, enable two-factor security, and never share your private keys. Research carefully and think long-term to stay safe.









