How Does Blockchain Work? A Beginner’s Guide to Blockchain Technology

Key Takeaways
- Blockchain secures data through encryption and decentralization.
- It links blocks to form a transparent ledger.
- Bitcoin was the first application of blockchain technology.
- Blocks store transactions, timestamps, and unique hashes.
- Distributed ledger technology prevents fraud and ensures transparency.
- Blockchain applications include finance, healthcare, and supply chain management.
Blockchain is changing industries worldwide. Its secure and transparent design transforms finance, healthcare, and supply chains. Let’s break it down step by step.
How Does Blockchain Work? A Beginner’s Guide
Blockchain is a decentralized ledger recording digital transactions. Think of it as a chain of blocks, each block holding data. Each block is securely linked, ensuring no tampering. This system runs without a central authority, ensuring transparency and security for all users.
Industries are embracing blockchain for its transformative power. The financial sector saves billions annually using blockchain for cross-border payments. Supply chains, like Walmart’s food safety program, use it to track products in real time. Blockchain helps prevent fraud, reduce paperwork, and improve efficiency.
Bitcoin, launched in 2009, was the first blockchain success. It introduced a peer-to-peer network for digital currency. Today, thousands of cryptocurrencies rely on blockchain technology to operate securely. This revolutionized not just money, but also how trust is built online.
Why Blockchain Matters Today
Blockchain’s decentralized design eliminates single points of failure. This means no one entity controls the system. In 2024, experts predict global blockchain spending will surpass $20 billion. Organizations use blockchain for secure, tamper-proof record-keeping, ensuring accountability across industries.
For example, healthcare providers use blockchain to store patient records securely. Imagine a world where your medical history can’t be altered or lost. Similarly, real estate transactions are becoming faster and safer with smart contracts.
Blockchain Applications: Real-World Impact
Blockchain is reshaping logistics, banking, and even art. In logistics, Maersk and IBM’s blockchain platform, TradeLens, tracks shipments across oceans. It reduces delays, enhances transparency, and lowers costs.
In banking, blockchain powers secure, instant cross-border payments. Ripple, for instance, allows banks to settle transactions in seconds, not days. Blockchain also makes stock trading more efficient, eliminating middlemen.
Even gaming is being disrupted. Blockchain-based games, like Axie Infinity, reward players with crypto. NFTs have created a $25 billion digital art market, revolutionizing ownership and creativity.
Why Blockchain Keeps Growing
The blockchain ecosystem is growing fast. Governments explore blockchain for voting systems, ensuring transparent elections. Companies use it to verify product authenticity, combating counterfeit goods. In 2024, over 80% of businesses report exploring blockchain solutions.
From tracking carbon footprints to enabling decentralized finance, blockchain is here to stay. It’s not just technology – it’s the foundation for trust in the digital age.
Key Components of Blockchain
Blocks and Transactions
Blocks are the building blocks of blockchain. Each block contains transaction data, a timestamp, and a unique hash. These hashes act like digital fingerprints, ensuring data security and integrity. If a single block is altered, its hash changes, breaking the chain and alerting the network.
Here’s how blocks function:
| Part | Description |
| Transaction Data | Details of the transaction |
| Timestamp | Time the transaction occurred |
| Hash | Unique code linking the block |
For example, if Alice sends 1 Bitcoin to Bob, the transaction data includes the amount, sender, and recipient. The timestamp records when it happened, and the hash secures it.
Cryptographic Hashes
Cryptographic hashes are the guardians of blockchain data. The widely used SHA-256 algorithm creates a unique, fixed-length hash for every block. Even a tiny change in data, like altering one letter, produces a completely new hash. This ensures data is tamper-proof.
Think of hashes as a lock, and the data is the key. If the data doesn’t match, the lock won’t work. This feature makes blockchain a fortress against fraud.
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
DLT ensures that every participant in the blockchain network has an identical copy of the ledger. This decentralization brings significant benefits:
- Real-time updates mean no delays.
- Fraud becomes nearly impossible with shared records.
- Transparent, secure transactions boost trust.
For instance, IBM’s Food Trust blockchain synchronizes data across the food supply chain. This helps trace contaminated items quickly, reducing health risks.
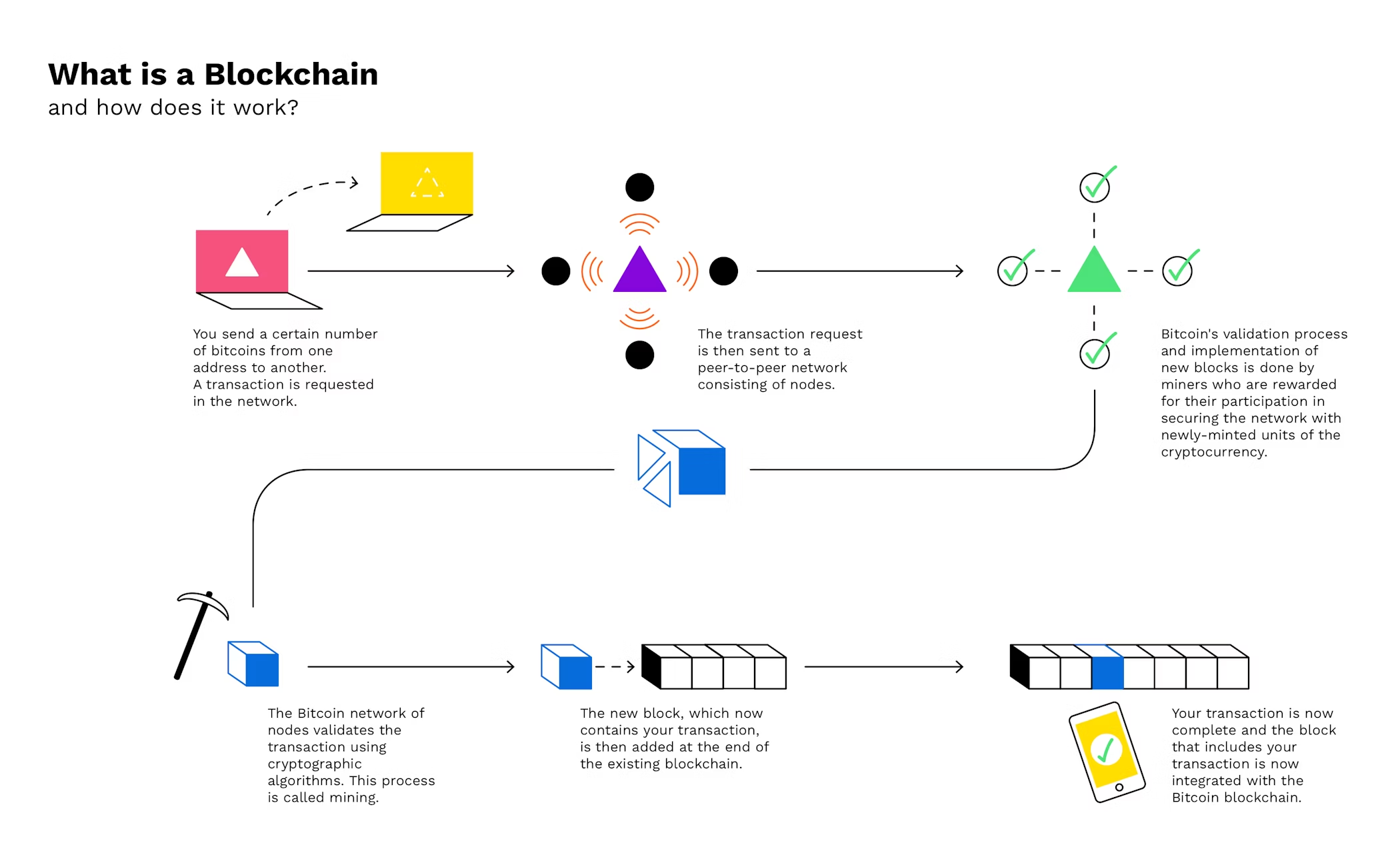
How Blockchain Works
Blockchain transactions follow a step-by-step process:
- A user initiates a transaction (e.g., buying Bitcoin).
- Network nodes validate the transaction using consensus mechanisms.
- Validated transactions are grouped into a block.
- The block is added to the blockchain.
- The ledger updates across all nodes in real-time.
This seamless process creates a transparent and secure digital record.
Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms ensure all participants agree on the validity of transactions. Here are two popular methods:
| Mechanism | Pros | Cons |
| Proof of Work | High security, decentralized | Energy-intensive, slow |
| Proof of Stake | Energy-efficient, scalable | Potential centralization |
For example, Bitcoin uses Proof of Work, requiring miners to solve complex puzzles. Ethereum 2.0 uses Proof of Stake, where validators are chosen based on their staked tokens, making it more eco-friendly.

Smart Contracts and Automation
Smart contracts are automated agreements that execute when specific conditions are met. These self-executing contracts run on blockchain platforms like Ethereum, enabling decentralized apps (dApps).
For instance, a smart contract could release payment to a freelancer once the agreed-upon task is completed. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, saving time and reducing costs.
Smart contracts also power decentralized finance (DeFi), offering services like lending and borrowing without banks. As of 2024, DeFi platforms manage over $100 billion in assets, showing their growing impact.
Blockchain’s combination of secure transactions, real-time synchronization, and automation is revolutionizing industries worldwide.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Cryptocurrency and Payments
Blockchain is the backbone of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Its decentralized nature ensures secure and transparent transactions. Key benefits include:
- Faster transactions with fees as low as a few cents.
- Decentralized systems that eliminate intermediaries like banks.
- Transparent records visible to all network participants.
For example, in 2024, Bitcoin processes over 350,000 daily transactions globally. Ethereum, with its smart contracts, powers decentralized apps (dApps) and finance (DeFi), handling millions of transactions daily. This speed and efficiency make blockchain crucial for digital payments.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain transforms supply chains by offering unparalleled transparency and efficiency. Businesses can trace every product from its origin to the consumer in seconds.
For instance:
- Walmart uses blockchain to track food origins, reducing foodborne illnesses.
- Fashion brands verify ethical sourcing of materials, ensuring sustainability.
- Pharmaceutical companies prevent counterfeit drugs by tracking shipments.
In 2024, over 70% of businesses in logistics report blockchain integration, saving billions annually by reducing fraud and delays.
Healthcare and Data Security
Blockchain secures sensitive patient data and streamlines healthcare processes. Its encrypted, decentralized system offers:
- Privacy-first medical records that patients control.
- Improved data sharing between hospitals and providers.
- Reduced risk of data breaches, saving millions in fines and lawsuits.
For example, Estonia uses blockchain to store health records for its citizens. This ensures real-time updates and data integrity, making healthcare more efficient and secure.
Other Emerging Use Cases
Blockchain goes beyond traditional industries, unlocking innovative possibilities like:
- NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens): Revolutionizing art and gaming with $25 billion in sales annually.
- DeFi (Decentralized Finance): Offering loans, savings, and investments without banks, with assets exceeding $100 billion.
- Digital Identity Management: Providing secure, verifiable IDs for online services and governance.
Even voting systems are being developed with blockchain to ensure transparency and trust. These use cases highlight the vast potential of this technology.
Advantages and Limitations of Blockchain
| Advantages | Limitations |
| High security | Scalability issues |
| Decentralization | High energy consumption |
| Transparency | Complex implementation |
Advantages
Blockchain’s high security ensures data is nearly impossible to tamper with. Decentralization removes the need for middlemen, reducing costs. Transparency builds trust among users, making it ideal for industries like finance, supply chains, and healthcare.
For example, the World Bank issued a blockchain-based bond, raising over $100 million while reducing costs and fraud risks.
Limitations
However, challenges remain. Scalability is a major concern, with networks like Bitcoin processing only 7 transactions per second, compared to Visa’s 24,000. Energy consumption is another issue, as Bitcoin mining alone uses more electricity than some countries.
Complex implementation also limits adoption, as integrating blockchain into legacy systems requires expertise and significant investment.
Despite these hurdles, blockchain continues to evolve, addressing these limitations with innovations like Ethereum’s Proof of Stake, which reduced its energy consumption by 99.95% in 2022.
Blockchain’s potential far outweighs its challenges, driving adoption across diverse industries in 2024.

The Future of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain’s future is shaping up to be transformative, addressing current limitations while unlocking new possibilities. Scalability and sustainability are at the forefront of its evolution. By 2024, the blockchain market is projected to grow beyond $60 billion, driven by technological advancements and increased adoption across industries.
Scalability: The Next Frontier
Current blockchain networks struggle to handle large volumes of transactions. Emerging solutions like layer-2 protocols and sharding aim to solve this. For instance:
- Ethereum 2.0 uses sharding to process transactions faster and more efficiently.
- Polygon and other layer-2 solutions offload transactions from the main chain, improving speed and reducing costs.
These advancements could make blockchain competitive with traditional systems like Visa, which handles thousands of transactions per second.
Sustainability: A Greener Blockchain
Energy consumption has been a major concern, especially for proof-of-work blockchains like Bitcoin. However, the industry is shifting toward eco-friendly solutions:
- Proof-of-stake systems, like Ethereum, drastically reduce energy use.
- Green mining initiatives harness renewable energy for blockchain operations.
- Carbon-neutral blockchain projects, such as Algorand, are gaining traction.
By 2024, over 50% of blockchain networks aim to integrate sustainable practices, addressing environmental concerns and attracting eco-conscious investors.
Integration with IoT
Blockchain is merging with the Internet of Things (IoT) to create smarter, more secure systems. This combination enables devices to communicate seamlessly while maintaining data integrity.
For example:
- In smart cities, IoT sensors track energy usage while blockchain secures the data.
- In supply chains, blockchain ensures IoT data is tamper-proof, improving efficiency.
By 2025, the global IoT-blockchain market could surpass $6 billion, revolutionizing industries from agriculture to transportation.

The Rise of DeFi and Tokenization
Decentralized finance (DeFi) continues to reshape financial systems. By 2024, DeFi platforms manage over $150 billion in assets. Key trends include:
- Yield farming: Offering users high returns through decentralized lending.
- Tokenized assets: Converting real-world assets like real estate into digital tokens, increasing accessibility and liquidity.
For instance, a $30 million Manhattan property was tokenized, allowing investors worldwide to buy shares.
Everyday Impact: Redefining Industries and Lives
Blockchain could soon touch every aspect of daily life. Examples include:
- Healthcare: Blockchain-secured vaccine records could streamline travel and medical care.
- Entertainment: Smart contracts ensure fair royalty payments for creators.
- Education: Blockchain credentials make verifying qualifications instant and trustworthy.
Even voting could become blockchain-based, ensuring transparency and reducing fraud in elections.
The future of blockchain is bright, promising innovation that redefines industries, empowers individuals, and addresses global challenges. It’s not just technology — it’s the foundation for a more secure, transparent, and connected world.
Conclusion: Why Blockchain Matters
Blockchain is revolutionizing how industries operate, offering unprecedented security and transparency. By 2030, blockchain is projected to add over $3 trillion in business value globally, making it one of the most transformative technologies of our time.
Its decentralized systems eliminate middlemen, reduce fraud, and enhance efficiency, making it indispensable in finance, healthcare, supply chains, and beyond. For instance, blockchain-powered systems are already saving companies billions annually by streamlining operations and increasing trust.
In a world increasingly driven by data, blockchain ensures that information is secure, immutable, and transparent. It provides the foundation for innovations like decentralized finance, NFTs, and tokenized assets, reshaping economies and creating new opportunities.
Understanding blockchain isn’t just for tech enthusiasts — it’s essential for anyone looking to thrive in the digital future. From protecting sensitive data to redefining transactions, blockchain is the backbone of tomorrow’s technology-driven world. Embracing it today means staying ahead in a rapidly evolving landscape.
What is blockchain in simple terms?
Blockchain is a secure, digital ledger for recording transactions.
How does blockchain ensure security?
It uses cryptographic hashes and decentralization to prevent tampering.
What industries use blockchain today?
Blockchain is used in finance, healthcare, and supply chain management.
What are smart contracts?
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements on the blockchain.
How is blockchain different from traditional databases?
Blockchain is decentralized, while traditional databases rely on central control.
Can blockchain replace traditional payment systems?
Blockchain offers faster, cheaper transactions but faces scalability challenges.
What is the role of miners in blockchain?
Miners validate transactions and add blocks to the chain.
How can beginners start learning about blockchain?
Read beginner guides, watch tutorials, and explore real-world use cases.




